axios 源码阅读
说在前面
说在前面
相信每位前端开发者或多或少都用过 axios 这个请求库,也一定再熟悉不过了。对于 axios 的内部实现原理笔者知之甚少,阅读 axios 源码的灵感也是看到了若川组织的源码共读活动,因此想要对 axios 的内部实现一探究竟。
参考地址
调试
chrome 调试浏览器环境的 axios
git clone https://github.com/lxchuan12/axios-analysis
cd axios
npm install
npm run start
# open http://localhost:3000
# chrome F12 source 控制面板 webpack// . lib 目录下,根据情况自行断点调试
本文是通过 sandbox/client.html 进行调试的。
axios 结构
打开控制台,在控制台打印一下 axios:
console.log({ axios: axios })
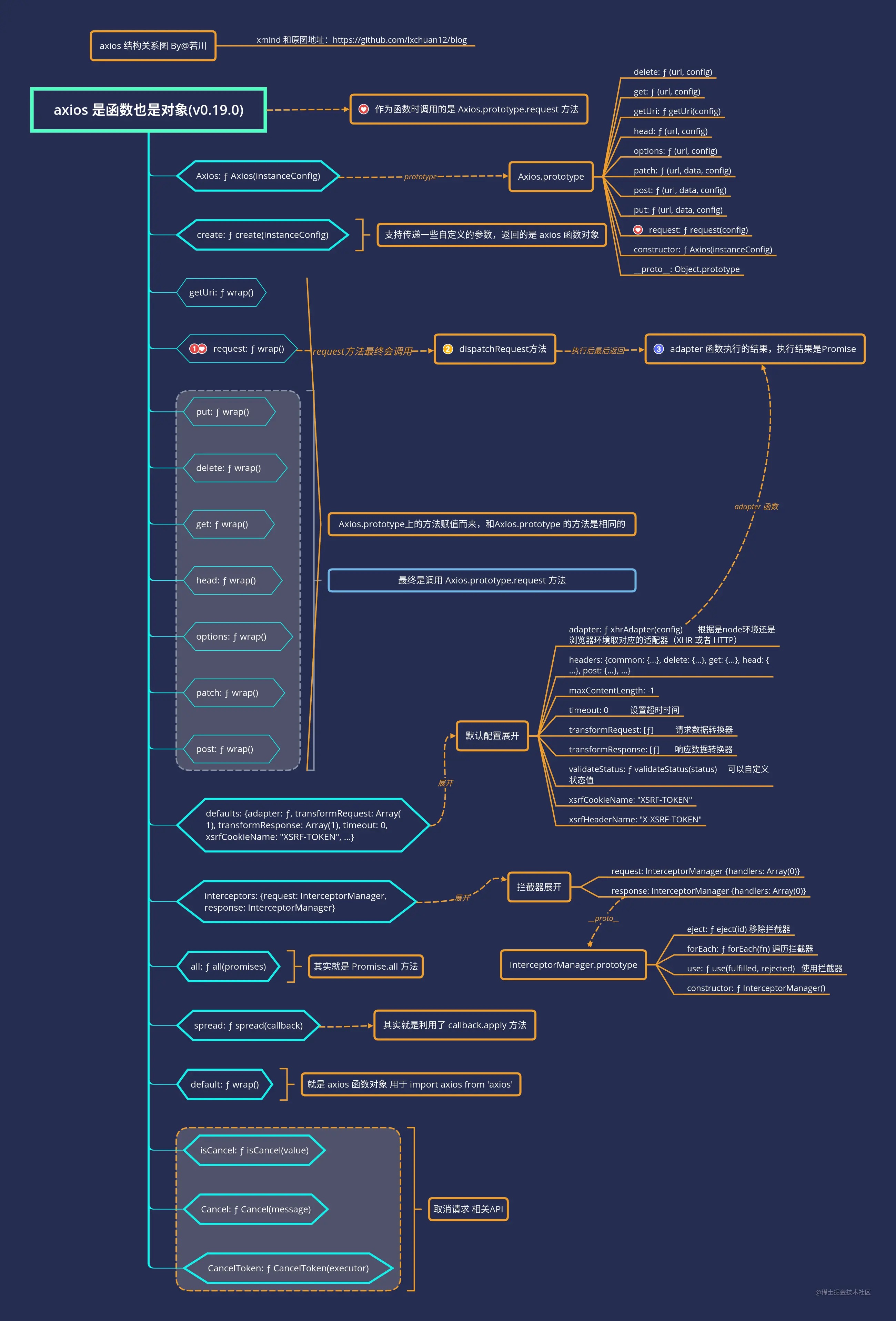
axios 源码分析
看源码的时候首先需要找到入口文件,对于小的项目还好,对于大型框架如 React 和 Vue,源码文件是非常多的,如果不能找到入口文件对于阅读源码是非常吃力的,因此找到入口文件是非常有必要的。
一般入口文件可以到 package.json 文件的 main 字段中查找,这里一般都会声明主入口文件:
{
"name": "axios",
"version": "0.19.0",
"description": "Promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js",
"main": "index.js",
...
}
主入口文件:
module.exports = require('./lib/axios')
从主入口文件可以看到,它引入的是 lib/axios,因此找到这个文件。
lib/axios 主文件
axios.js 主要做的事包括:
- 引入工具函数,如:utils,Axios 构造函数,defaults 默认配置等。
- 创建实例,生成实例对象 axios,axios.create,axios.Axios 等。
- 取消相关 API 实现以及 all,spread,exports(导出)。
引入工具函数相关
// 引入 utils 对象
var utils = require('./utils')
// 引入bind方法
var bind = require('./helpers/bind')
// 引入核心构造函数
var Axios = require('./core/Axios')
// 引入合并配置方法
var mergeConfig = require('./core/mergeConfig')
// 引入默认配置
var defaults = require('./defaults')
创建实例相关
/**
* Create an instance of Axios
*
* @param {Object} defaultConfig The default config for the instance
* @return {Axios} A new instance of Axios
*/
function createInstance(defaultConfig) {
// new Axios生成一个实例对象
var context = new Axios(defaultConfig)
// 调用bind方法改变context的this指向,指向Axios.prototype.request
// 这也就是为什么调用axios的时候,其实调用的是Axios.prototype.request函数的原因了
var instance = bind(Axios.prototype.request, context)
// Copy axios.prototype to instance
// 复制 Axios.prototype 到实例上。
// 这也就是为什么会有axios.get方法,且实际上调用的是Axios.prototype.get方法
// 相当于Axios.prototype有的方法,都可以使用axios. 这种形式调用
utils.extend(instance, Axios.prototype, context)
// Copy context to instance
// 复制 context 到 intance 实例
// 也就是为什么默认配置 axios.defaults 和拦截器 axios.interceptors 可以使用的原因
utils.extend(instance, context)
// 返回实例对象
return instance
}
// 导出 创建默认实例
var axios = createInstance(defaults)
// 暴露 Axios calss 允许 class 继承
axios.Axios = Axios
// 工厂模式 创建新的实例 用户可以自定义一些参数
axios.create = function create(instanceConfig) {
return createInstance(mergeConfig(axios.defaults, instanceConfig))
}
bind 函数
// bind接收两个参数,分别是函数和thisArg指向
module.exports = function bind(fn, thisArg) {
return function wrap() {
// 把参数生成数组
var args = new Array(arguments.length)
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
args[i] = arguments[i]
}
// apply方法接收两个参数,第一个参数是要调用的this参数,第二个参数是函数的参数数组
// 调用返回参数结构
return fn.apply(thisArg, args)
}
}
extend 函数
extend 函数的主要作用就是复制对象
function extend(a, b, thisArg) {
forEach(b, function assignValue(val, key) {
if (thisArg && typeof val === 'function') {
a[key] = bind(val, thisArg)
} else {
a[key] = val
}
})
return a
}
其实就是遍历 b 对象,将其复制到 a 对象中,如果是函数的话,就用 bind 调用。
forEach 函数
/**
* Iterate over an Array or an Object invoking a function for each item.
*
* If `obj` is an Array callback will be called passing
* the value, index, and complete array for each item.
*
* If 'obj' is an Object callback will be called passing
* the value, key, and complete object for each property.
*
* @param {Object|Array} obj The object to iterate
* @param {Function} fn The callback to invoke for each item
*/
function forEach(obj, fn) {
// 判断 null 和 undefined 直接返回
if (obj === null || typeof obj === 'undefined') {
return
}
// 如果不是对象,放在数组里。
if (typeof obj !== 'object') {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
obj = [obj]
}
// 是数组 则用for 循环,调用 fn 函数。参数类似 Array.prototype.forEach 的前三个参数。
if (isArray(obj)) {
// Iterate over array values
for (var i = 0, l = obj.length; i < l; i++) {
fn.call(null, obj[i], i, obj)
}
} else {
// 用 for in 遍历对象,但 for in 会遍历原型链上可遍历的属性,所以用 hasOwnProperty 来过滤自身属性了。
// 其实也可以用Object.keys来遍历,它不遍历原型链上可遍历的属性。
for (var key in obj) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
fn.call(null, obj[key], key, obj)
}
}
}
}
如果对 Object 相关 API 不熟悉的,可以参考我的文章-JS 对象方法
取消相关 API
// 导出 Cancel 和 CancelToken
axios.Cancel = require('./cancel/Cancel')
axios.CancelToken = require('./cancel/CancelToken')
axios.isCancel = require('./cancel/isCancel')
axios.all = function all(promises) {
return Promise.all(promises)
}
axios.spread = require('./helpers/spread')
module.exports = axios
//以下的使用默认导出也就是为什么可以使用 import axios from 'axios'; 来引入axios了
module.exports.default = axios
spread 函数
spread是一个用于调用函数和扩展参数数组的语法糖。
对于以下的需求:
function f(x, y, z) {}
var args = [1, 2, 3]
f.apply(null, args)
可以直接使用 spread 语法糖实现:
spread(function (x, y, z) {})([1, 2, 3])
源码实现如下:
/**
* @param {Function} callback
* @returns {Function}
*/
module.exports = function spread(callback) {
return function wrap(arr) {
return callback.apply(null, arr)
}
}
核心构造函数 Axios.js
/**
* Create a new instance of Axios
*
* @param {Object} instanceConfig The default config for the instance
*/
function Axios(instanceConfig) {
// 设置默认参数
this.defaults = instanceConfig
// 拦截器
this.interceptors = {
// 请求拦截器
request: new InterceptorManager(),
// 响应拦截器
response: new InterceptorManager()
}
}
Axios.prototype.request
Axios.prototype.request实现的步骤如下:
- 判断第一个参数是否是 string,如果是 string,则设置 url,即支持 axios('example/url', [, config])和 xios({})两种请求方式。
- 合并默认参数和用户传入的参数
- 设置请求方法,默认为 get 请求方法
- 将用户设置的请求和响应拦截器、发送请求的 dispatchRequest 组成 Promise 链,最后返回还是 Promise 实例。也就是保证了请求前拦截器先执行,然后发送请求,再响应拦截器执行这样的顺序。
/**
* Dispatch a request
*
* @param {Object} config The config specific for this request (merged with this.defaults)
*/
Axios.prototype.request = function request(config) {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
// Allow for axios('example/url'[, config]) a la fetch API
// 下面的代码其实就是相当于可以以axios('example/url'[, config])方式调用,即如果config是string类型,那么第一个参数是url
if (typeof config === 'string') {
config = arguments[1] || {}
config.url = arguments[0]
} else {
config = config || {}
}
// 合并默认参数和用户传入的参数
config = mergeConfig(this.defaults, config)
// Set config.method 设置请求方法,默认是get请求
if (config.method) {
config.method = config.method.toLowerCase()
} else if (this.defaults.method) {
config.method = this.defaults.method.toLowerCase()
} else {
config.method = 'get'
}
// Hook up interceptors middleware
// 组成`Promise`链 ,返回Promise实例
// 把 xhr 请求 的 dispatchRequest 和 undefined 放在一个数组里
var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined]
// 创建一个请求实例,相当于 new Promise(config)
var promise = Promise.resolve(config)
// 遍历所有请求拦截器,放在chain的前面
this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(interceptor) {
chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected)
})
// 遍历所有响应拦截器,push到chain的后面
this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(interceptor) {
chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected)
})
// 遍历chain数组,直到遍历chain.length为0
while (chain.length) {
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift())
}
return promise
}
dispatchRequest
/**
* Dispatch a request to the server using the configured adapter.
*
* @param {object} config The config that is to be used for the request
* @returns {Promise} The Promise to be fulfilled
*/
module.exports = function dispatchRequest(config) {
// 取消相关
throwIfCancellationRequested(config)
// Ensure headers exist 确保headers存在
config.headers = config.headers || {}
// Transform request data 转换请求的数据
// transformData 就是遍历数组,调用数组里的传递 data 和 headers 参数调用函数,返回数据。
config.data = transformData(config.data, config.headers, config.transformRequest)
// Flatten headers 拍平config.headers
config.headers = utils.merge(
config.headers.common || {},
config.headers[config.method] || {},
config.headers || {}
)
// 删除一些 config.header。 以下这些方法 删除 headers
utils.forEach(
['delete', 'get', 'head', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'common'],
function cleanHeaderConfig(method) {
delete config.headers[method]
}
)
// 返回适配器adapter(Promise实例)执行后 then执行后的 Promise实例。返回结果传递给响应拦截器处理。
var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter
return adapter(config).then(
function onAdapterResolution(response) {
throwIfCancellationRequested(config)
// Transform response data
response.data = transformData(response.data, response.headers, config.transformResponse)
return response
},
function onAdapterRejection(reason) {
if (!isCancel(reason)) {
throwIfCancellationRequested(config)
// Transform response data
if (reason && reason.response) {
reason.response.data = transformData(
reason.response.data,
reason.response.headers,
config.transformResponse
)
}
}
return Promise.reject(reason)
}
)
}
adapter 适配器
var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter
根据上述代码的 adapter,用户可以自定义 adapter,没有自定义 adapter 的话,就使用默认的 adapter,接着看 defaults.adapter,即在文件夹:axios/lib/defaults.js
对于浏览器引入 xhr,对于 node 环境则引入 http。
function getDefaultAdapter() {
var adapter
if (typeof XMLHttpRequest !== 'undefined') {
// For browsers use XHR adapter
adapter = require('./adapters/xhr')
} else if (
typeof process !== 'undefined' &&
Object.prototype.toString.call(process) === '[object process]'
) {
// For node use HTTP adapter
adapter = require('./adapters/http')
}
return adapter
}
var defaults = {
adapter: getDefaultAdapter()
...
}
拦截器 InterceptorManager
function InterceptorManager() {
this.handlers = []
}
handlers用于存储拦截器函数。另外,它还声明了三个方法,分别是 use,eject,forEach.
拦截器使用
// 添加请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(
(config) => {
return config
},
(err) => {
return Promise.reject(err)
}
)
// 添加响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
return response
},
(err) => {
return Promise.reject(err)
}
)
如果想要移除请求拦截器,那么可以使用 eject 方法,如下所示:
const myRequestInterceptors = axios.interceptors.request.use(function () {})
axios.interceptors.request.eject(myRequestInterceptors)
InterceptorManager.prototype.use
/**
* Add a new interceptor to the stack
*
* @param {Function} fulfilled The function to handle `then` for a `Promise`
* @param {Function} rejected The function to handle `reject` for a `Promise`
*
* @return {Number} An ID used to remove interceptor later 返回ID 是为了用 eject 移除
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function use(fulfilled, rejected) {
this.handlers.push({
fulfilled: fulfilled,
rejected: rejected
})
return this.handlers.length - 1
}
传递两个函数作为参数,返回 ID,用于之后 eject 移出。
InterceptorManager.prototype.eject
/**
* Remove an interceptor from the stack
*
* @param {Number} id The ID that was returned by `use`
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.eject = function eject(id) {
if (this.handlers[id]) {
this.handlers[id] = null
}
}
根据 use 返回的 ID 移除 拦截器。
InterceptorManager.prototype.forEach
/**
* Iterate over all the registered interceptors
* @param {Function} fn The function to call for each interceptor
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.forEach = function forEach(fn) {
utils.forEach(this.handlers, function forEachHandler(h) {
if (h !== null) {
fn(h)
}
})
}
遍历执行所有拦截器,传递一个回调函数(每一个拦截器函数作为参数)调用,被移除的一项是 null,所以不会执行,也就达到了移除的效果。
 meixiu
meixiu